
This factor scales down the velocity profile. This is called the “exposure correction factor”. As the coastal wind has a lower roughness, the profile is steeper and thus at 10 meters height is already much closer to its maximum speed.įor the wind comfort calculation, we actually take into account that the wind would slow down when it comes from the coastal area and reaches urban levels, for example. The figure above shows the ABL profile that needs to be applied during the CFD/wind comfort analysis. SimScale gives you the control of exposure for every direction.Įxposures can be defined in the Wind conditions space in a drop down box as depicted below:įigure 5: Atmospheric boundary layers with different exposure categories This might be, for example, Urban area in all directions if simulating a region within The City of London, or Coastal area for some directions and Urban area or Suburban area for the remaining when simulating a coastal city like Miami, Florida. Different terrains cause different velocity gradient vertical to the ground commonly referred to as the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) which can be a topic on its own, but for PWC analysis, its definition is as simple as defining the exposure category that corresponds to the surroundings outside of the simulation extent. Wind exposures essentially control how the wind speeds vary due to the presence of specific terrain characteristics. Please follow this knowledge base article for more information.

Surface roughness can have a significant impact on wind comfort results. Additionally, you can also add surface roughness to specific faces and volumes under the Advanced modelling node in the pwc simulation tree. Surface roughness can also be applied outside the region of interest by toggling-on the Add surface roughness option. We are therefore unable to control or predict which direction the airport will be operating in.Figure 3: Generated wind rose from imported data for 16 directions Surface Roughness The weather forecast is not always a reliable indicator of what is happening at Heathrow since the Met Office forecast for the public relates to ground level.ĭue to the direction of operation being determined by the wind, the operation can change direction more than once in a day. The position is kept under constant review. The direction of operation is determined by NATS air traffic controllers who monitor wind speed and direction on the airfield and at different levels up to 3,000ft. We provide live updates on the direction Heathrow is operating via our website and Twitter feed (follow us Who monitors the wind direction at Heathrow? The percentage of westerly and easterly operations varies from week to week and month to month. We can only do this when the wind direction allows us to or is below 5 knots. This means that instead of westerly preference at night, we rotate between westerly and easterly operations to provide a fairer distribution of aircraft noise to the east and west of the airport.
This is known as ‘westerly operations’.įollowing consultation in 2001, the Government decided that the westerly preference should be removed at night and particularly during the early morning period when there are more arrivals than departures. That means that with a westerly preference in place the majority of aircraft (approximately 70% a year) arrive from the east (over London) and take off towards the west (over Berkshire/Surrey).
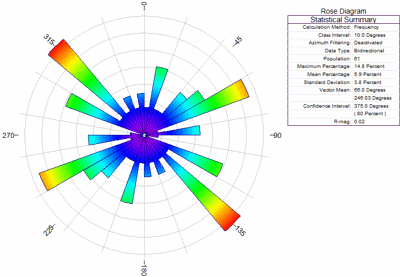
In the UK, the wind is mostly from the south west. This was when departures were considered to be more disruptive to local communities than arrivals. This was introduced in the 1960s to reduce the number of aircraft taking off in an easterly direction over London, the most heavily populated side of the airport. This is Government policy and means that even during periods of light easterly winds aircraft will continue to land in a westerly direction, making their final approach over London. What is ‘westerly preference’?ĭuring the day, a ‘westerly preference’ is operated at Heathrow. At Heathrow, winds are light on average 20% of the time.

These are called a "directional preference" and they say in which direction operations should be when the winds are light and there is a choice. Rules are set by Government to determine what to do in these circumstances. When winds are light (below 5 knots – about 6 miles per hour) aircraft can potentially take off or land in either direction. This is because an aircraft’s wing relies on the speed of the air moving over it (airspeed) to lift it off the ground. For safety and performance reasons aircraft typically take off and land into the wind. The direction planes fly at Heathrow depends on the direction of the wind.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
